The Leven and Melville Papers
The project's first set of data came from the Leven and Melville Papers which are a printed collection of recorded discussions and decisions made by individuals, civil servants, and officials in the nascent Williamite regime during the Revolution and early 1690s. This particular collection is that of the Secretary of State for Scotland - George Melville and includes 599 letters sent between the years of 1689 and 1691 and contain communication between the monarch’s secretary and the monarch, local officials, communications from overseas, instructions, intercepted correspondence, and much more. The physical manuscript papers are held at the National Records for Scotland as part of the wider Papers of the Leslie Family, Earls of Leven and Melville (1200-1936) in Edinburgh, Scotland. The correspondence has been since digitized as a print book which is available online at the Internet Archive and Electric Scotland which has become a digital surrogate for the manuscript papers. The project now includes correspondence from the larger collection at the National Records for Scotland including material from the Jacobite Papers.
Degree Centrality
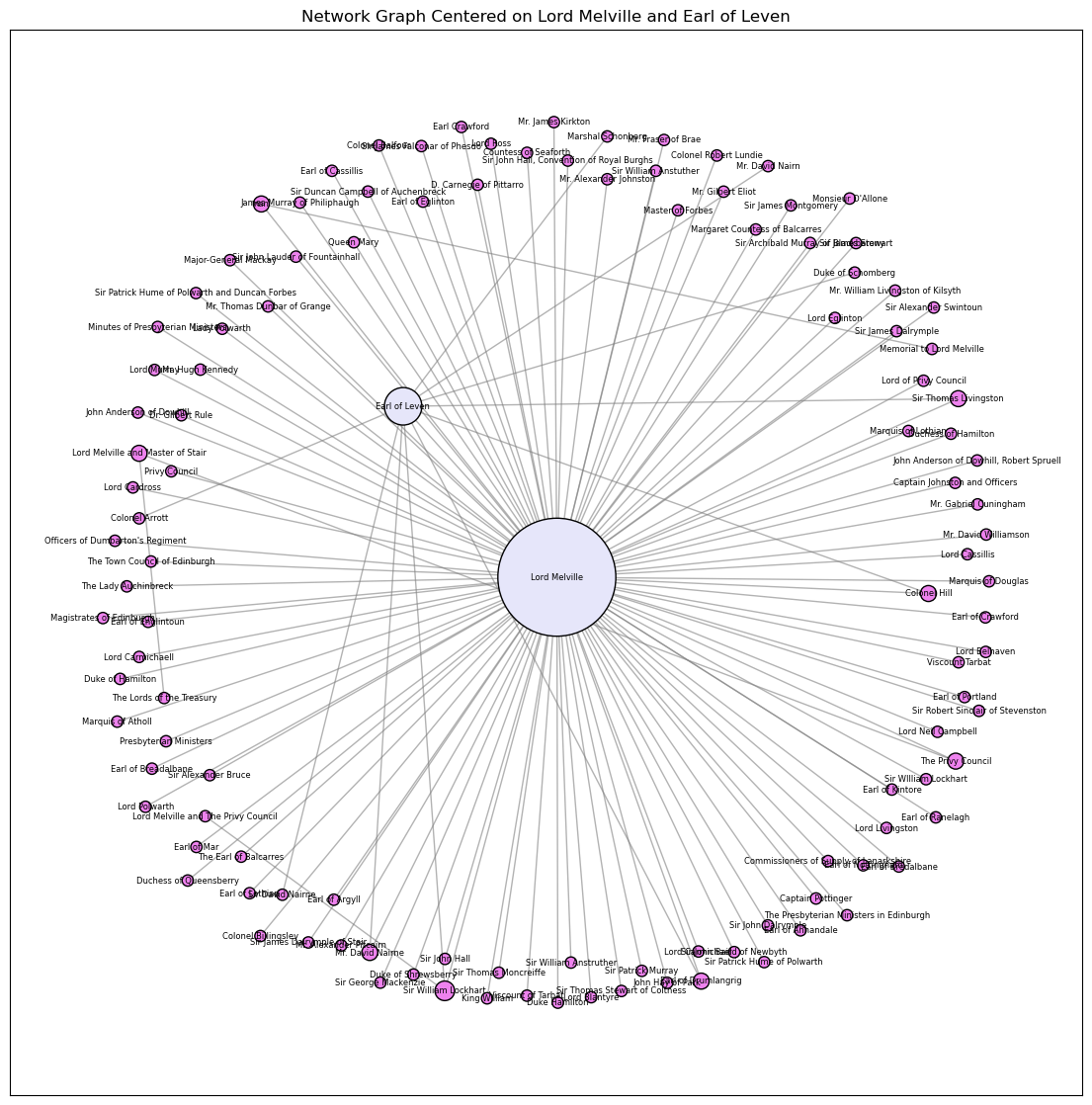
Our network analysis of the Melville Correspondence began with degree centrality of the correspondence throughout the wider papers. This is a calculation of the number of edges or connections of a singular node. Degree centrality is the easiest calculation of the significance of the node on the network i.e. where it is structurally important and often reveals clusters that dominate the network. Unsurprisingly, Melville has the largest centrality count, followed by King William, the Privy Council, and the Earl of Leven with another interesting node where the sender was unknown. This measure is useful for thinking about hierarchy and power dynamics within the new regime. Many people wrote to the Secretary of State for many different reasons, most commonly individuals wrote asking for favor or giving updates or opinions on the ongoing situation in Scotland-whether that was the Highland War, the siege in Londonderry, or difficulties in parliament or settling the religion. For example, Thomas Livingston wrote to Melville in 1691 saying "Since my last [letter], there is nothing occured of moment here... We have the news here that four French men of war are come to the Isle of Skye, and brought ammunition, arms, provisions, and officers."1 This overview is important since Melville was directly connected to the King and his primary source of information about Scotland's affairs, even into 1691 when things were supposedly cooling down. This corpus is highly skewed toward Melville and Leven.
What we have found within these papers 307 unique persons, 47 unique groups, and 14 organizations; each was assigned metadata in the form of their allegiance, cabinet position, and weight. The Leven and Melville papers printed corpus contained 72 places of origin and target which were then geocoded. We argue similarly to Ruth and Sebastian Ahnert's suggestions that network hubs correspond broadly with the centers of government.2 This also includes somewhat symbolic hubs of the monarch and the principal secretaries - primarily their residences and work places this for example might be Holyrood Palace, Kensington Palace, or Tarbat House. There are imbalances present throughout the corpus especially since more letters received survive than letters sent. If there was a complete record of the correspondence, there would be less imbalance. There are also intercepted letters present in the collection which might account for some of the anomalies in the network.
After some initial calculations and experimentations, we argue that based on the letters contained in the corpus the most connected nodes are Melville, King William, Queen Mary, William Lockhart, the Earl of Leven, Colonel Canon (Jacobite General) and the Privy Council. This is unsurprising since the monarch and their principal secretaries tend to be the same epistolary hub. The Privy Council served as the primary contact for the Scottish administration for much of the period. William Lockhart served as Solicitor General for Scotland from 1689 to 1693 and was the King's principal legal advisor for Scottish affairs. Leven and Canon served as important military officials and had many connections and networks. That these are the most connected nodes speaks to the number of letters that were exchanged about the evolving situation in Scotland. Despite instructions contained within many of the letters, which told the receiver to burn the letter received, correspondence from the period has survived. In aggregate, it shows that despite previous assertions that William was not interested what was going on in his northern kingdom we can argue that this seems not to be the case.
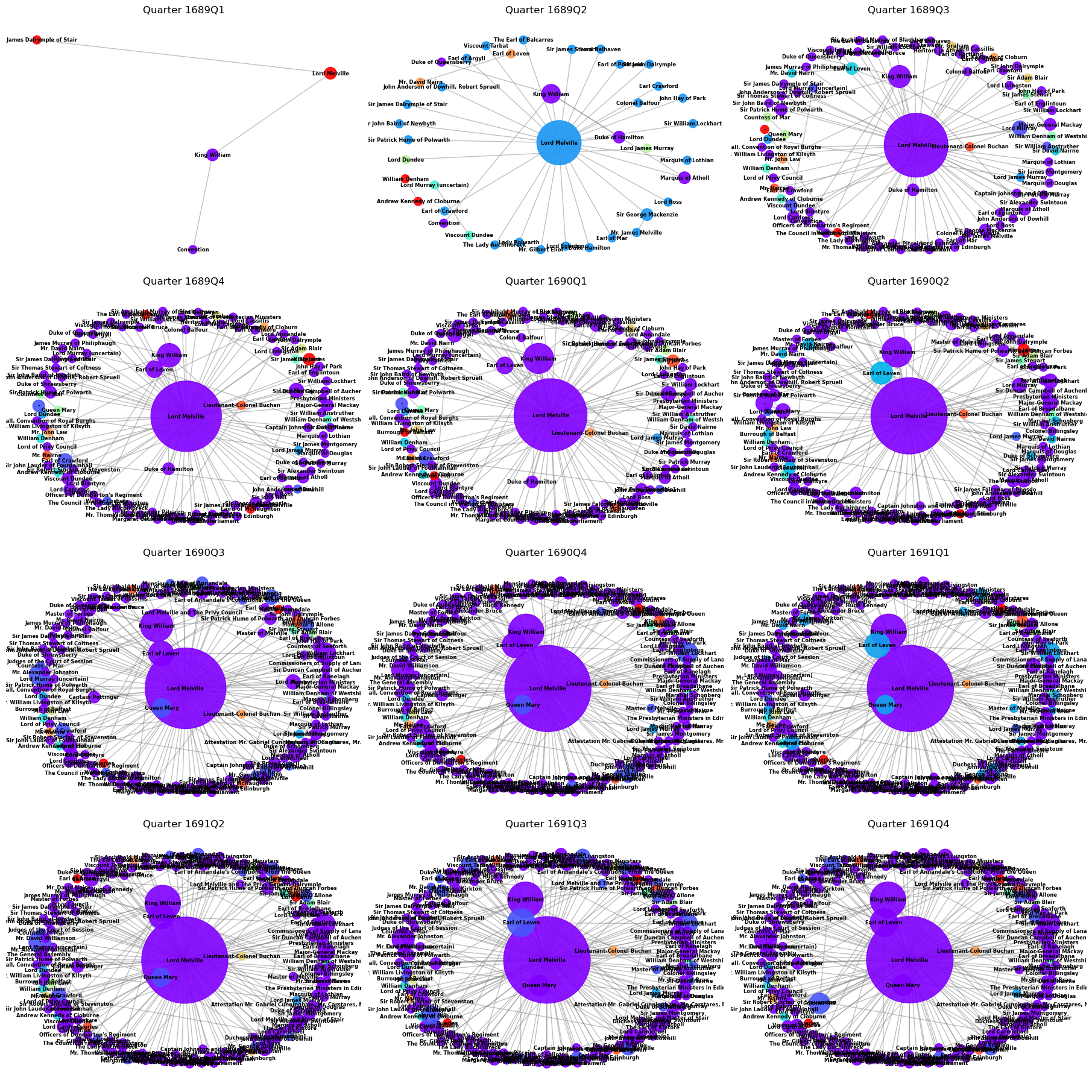
The subplots here show quarterly accounts of the communications in the Leven and Melville Papers over the course of the revolutionary period. The plots which match Melville - in purple or violet - are all directly connected to Melville and either sent or received a letter from him. Those nodes in other colors are the outliers that either corresponded only with another node in the collection or are letters that were intercepted by the Secretary of State's employees. As Melville's network becomes denser, his receiving node grows, indicating that he received more letters over time. This correspondence activity reached its peak density in the fourth quarter of 1690 and maintained that density throughout 1691. The Earl of Leven on the graph is also connected to Melville since they are related and exchanged letters. They are also indirectly connected by multiple bridges and social spheres different social spheres. For example, the Duke of Hamilton as High Commissioner to the Scottish Parliament in 1689, acts as a bridge between them. The plots are also directional and show the direction of communications as Melville appears as both a node for sending and receiving letters. Melville received 447 letters over the course of the corpus but only sent 31 whereas the Earl of Crawford sent 81 letters and received 6 (but this might speak more to the practices of privacy between elite correspondence in the 17th century). As a node, Melville has the highest infrastructural role in the network, followed by the Duke of Hamilton (High Commissioner to the Scottish Parliament), his successor the Earl of Crawford, and then the monarch himself. The diagrams also indicate an increased density of networks over time. It also shows the density of specifically the Williamite network since the early part of 1689 contained many Jacobite sympathizers (which is why we see the Viscount of Dundee, James's military general and Lord Murray), and their names seem to disappear over time while Melville's centrality to the network grows as we see his purple node growing larger from 1689 through 1691.
Geography and Place
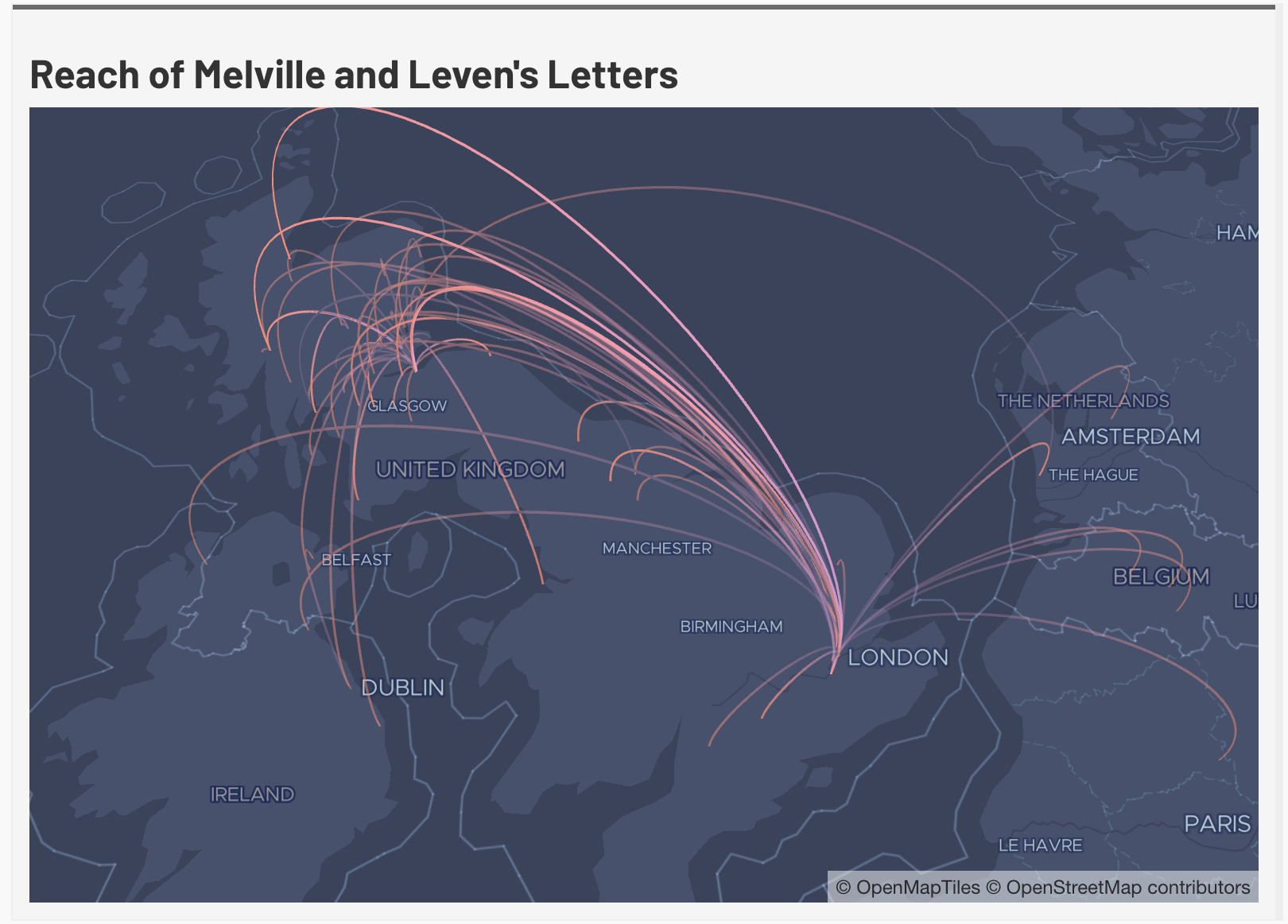
Mapping the network has different implications. Structural significance is just as important as geographical space. As Ruth and Sebastian Anhert have noted, an individual’s importance to a network can often be defined by their actual geographical position, especially if they are a diplomat.3 Letters let us see large-scale networks over space and time. Of the letters in this corpus the vast majority list their place of sending and intended destination. More than that they show the reaches of one central node in the network. Melville was receiving letters from all over the British Isles as well as the continent. Despite the fact that William never set foot in Scotland, the considerable two-way flow of correspondence between Edinburgh and London, combined with the numerous journeys made by officers of state, meant that he had a great deal of information about the situation in Scotland and was able to relay instructions to his Scottish counterparts. The high traffic of post and letters referring to the situation in Scotland suggests that the secretaries stayed in frequent contact with their counterparts in Edinburgh. One of the things that is evident from the graph produced by the Leaflet libraries is that the network expanded more than just Scotland and England, letters in Melville's corpus ranged from Dublin and Ballyhara in Ireland to Brussells and Gerpines on the continent. The largest clusters were in Edinburgh and London which is unsurprising since William's most important ministers resided in the respective capitals and centers of governance. Smaller clusters existed at both Tarbat and Fort William, the latter became a very important node of the military campaign from 1690 to 1691. The flurry of letters and a memorial to Melville from the Viscount of Tarbat between June and July in 1689 accounts for the other smaller cluster. The letters stemming from Ireland can be accounted for both by the intercepted letters from James and William's travels before and after the Battle of the Boyne.
Keywords
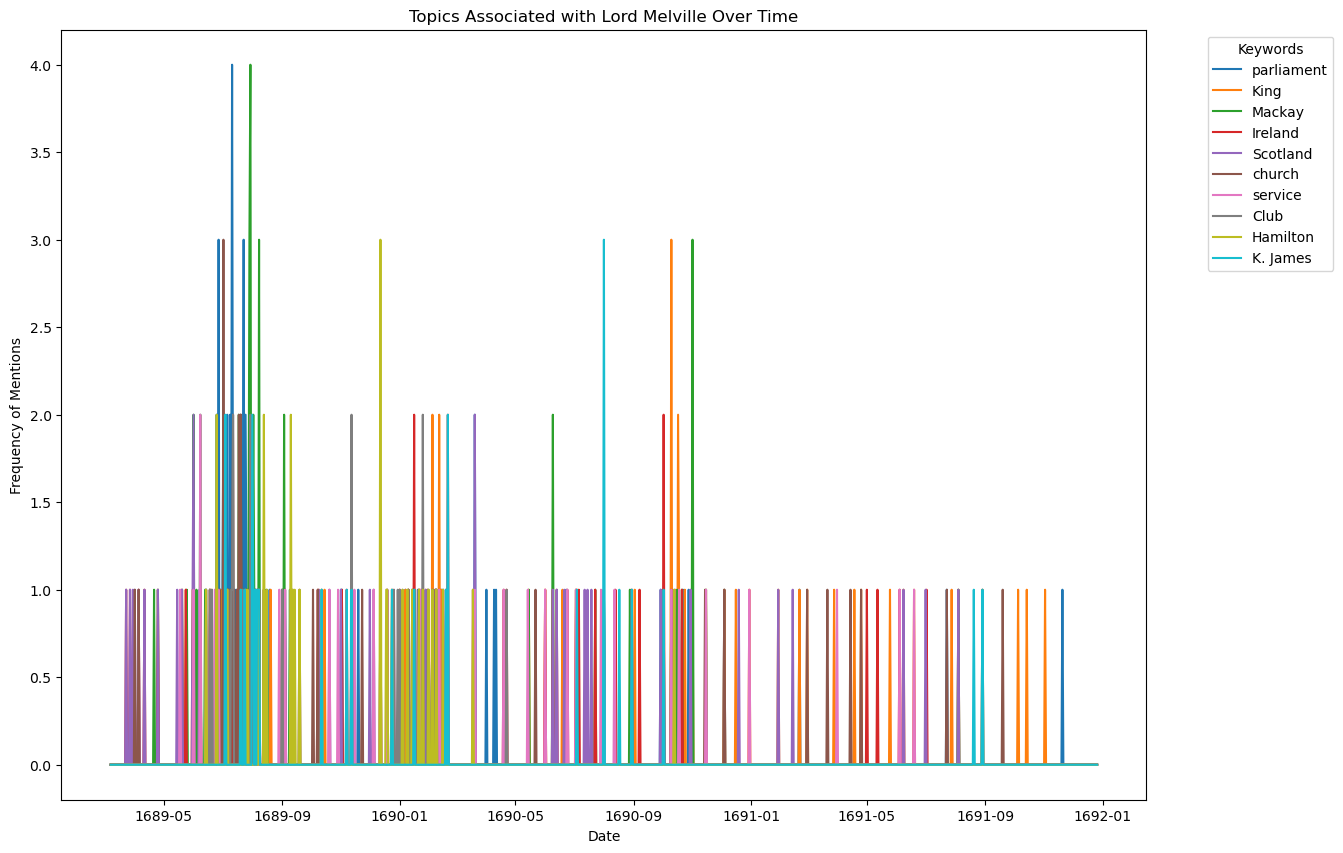
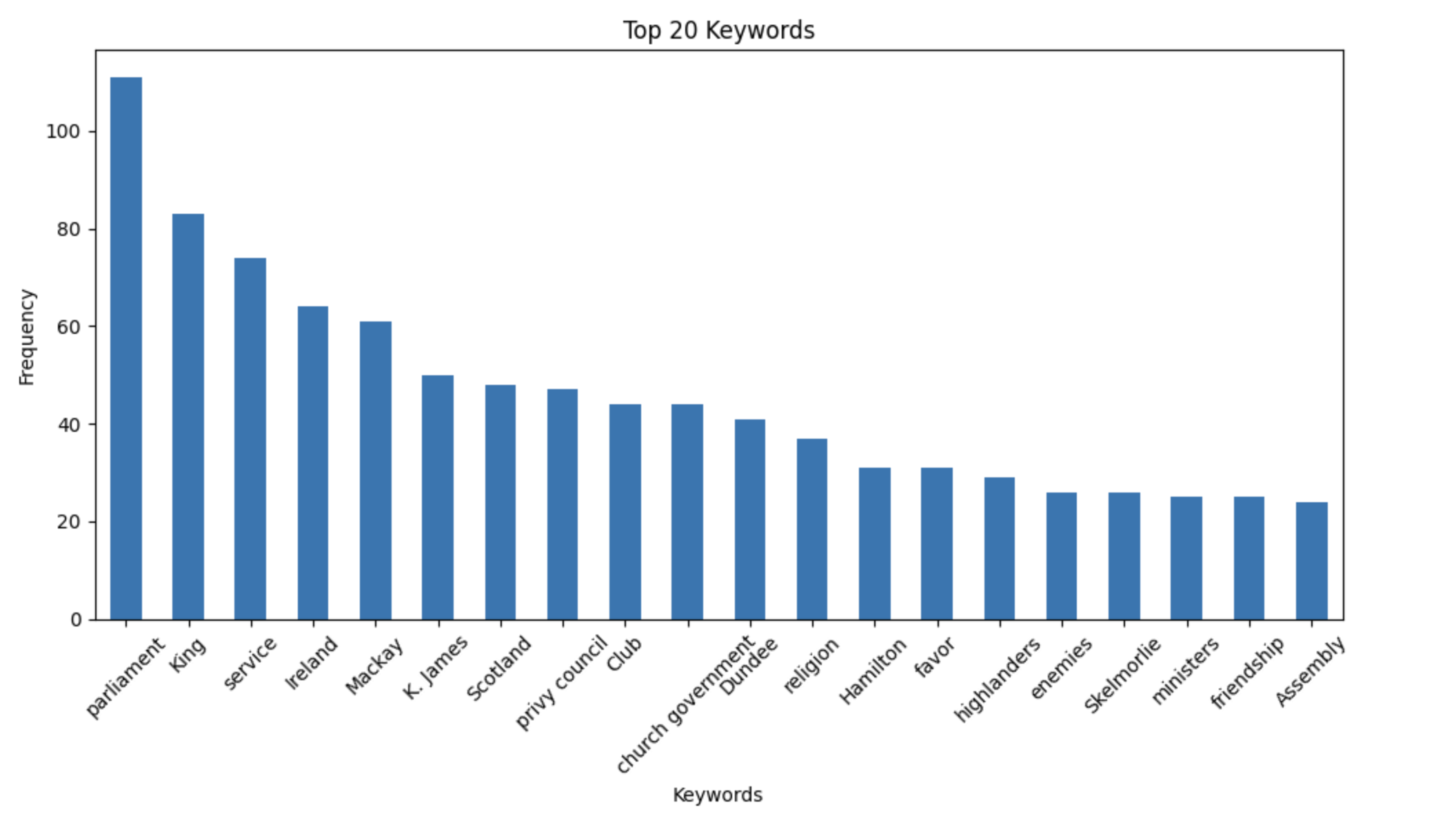
Moving into the actual content of the letters, we have calculated a summary of key words for each of the letters represented in the corpus. These key words are a valuable source of information for what individuals were talking about in their letters. Since the letters have been both transcribed and digitized, they are a ripe source for topic modelling and text analysis. Therefore, we can trace the topics and news that was deemed important between correspondents. There were up to seven keywords assigned to each letter and we tracked this over the course of the years 1688 to 1692. We did this over time because often the most common words were associated with the monarchy. This list will not likely lead us to the events happening at the time.
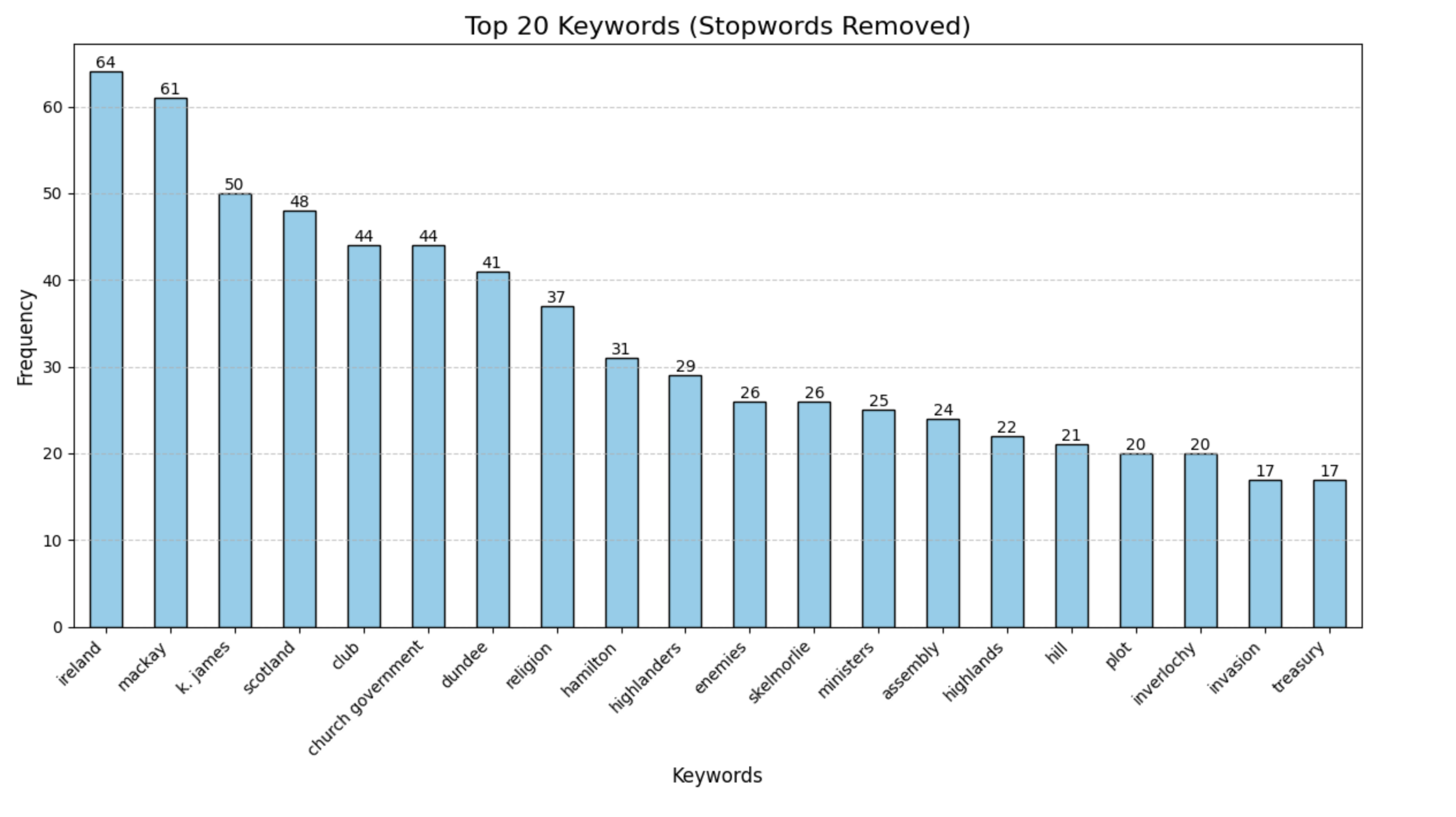
The most common topic over the course of the period was parliament, which is somewhat unsurprising given the rise of the supremacy of parliament over the monarchy. What this list does tell us is that over the course of the letter exchange period Melville - and his network - were very interested in the events in Scotland and Ireland. We did this analysis by extracting a list of ranked keywords based on frequency in the total number of letters. We did this without a stoplist and with a stop list. The reason we did this is because the notations made in letters about favor to the secretary, service to the monarchy, and fluctuating usage of terms related to the monarchy don't have an impact on our analysis. We are more interested in the content out with that scope including events and concerns during the chaos of Revolution. The keywords analysis without the stopword list included 6 topics related specifically to the monarchy and governance (parliament, privy council, King, service, favor, friendship) which at the time was under debate and shows that the Secretary was engaged in discussions over governance and appointments. However, when the words related to governance and the monarchy are removed from the dataset, we can see that the topics reflect major events across the four-year period including the suspected invasion, Ireland, and the movements of Dundee and the highlanders.
- Sir Thomas Livingston to George Melville, 13th June 1691 The Leven and Melville Papers p.621.
- Ruth Anhert and Sebastian Anhert, Tudor Networks of Power (Oxford, 2023), p.28
- Anhert and Anhert, Tudor Networks of Power, p.205.